Narcan: Uses, Effects, and Safety Guide
Share
Narcan is a life-saving medication used to reverse an opioid overdose. Understanding how to use Narcan, its effects, and potential side effects is crucial, especially in emergencies. This guide will help you grasp the importance of Narcan and how it can be used effectively to save a life.
What is Narcan, and How Does It Work?
Narcan, known by its brand name Narcan, is designed to reverse the effects of an opioid overdose. Opioids, including prescription opioids like oxycodone and fentanyl, can dangerously slow or stop breathing, leading to loss of consciousness. Administering Narcan quickly can block these effects, helping the person start breathing again and regain consciousness.
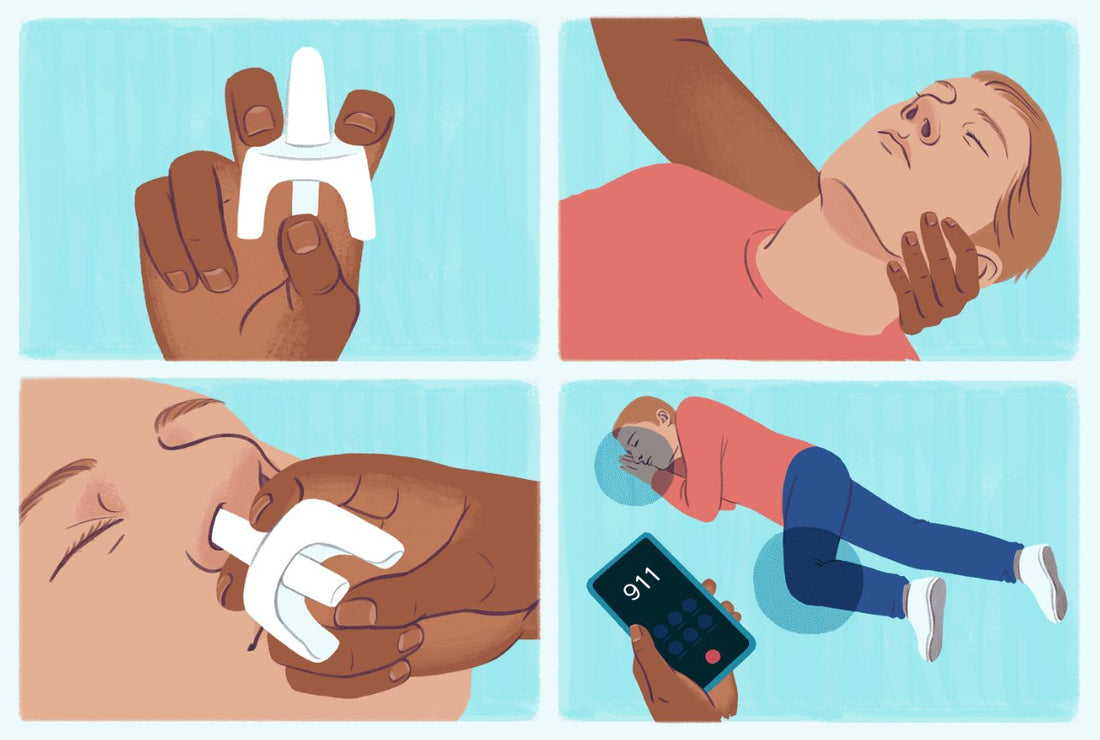
Narcan works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain, pushing out the opioids and stopping their effects. This action is critical in emergencies, as it can reverse the overdose and restore normal breathing. Narcan is available in two forms: a nasal spray and an injection. The nasal spray, also known as Narcan nasal spray, is easy to use and ideal for people without medical training. The injection form is commonly used by healthcare professionals and first responders. You can administer the injection into a muscle, under the skin, or directly into a vein, depending on the situation and your level of training.
Administering Narcan: What to Expect
When administering Narcan, the person receiving it may begin to wake up and breathe normally within minutes. However, the effects can be temporary, so it’s essential to seek immediate medical help after administering a single dose. If the person does not respond to the first dose of Narcan, a healthcare professional may need to administer additional doses.
Understanding how to administer Narcan correctly can make all the difference in an emergency. If you’re using Narcan nasal spray, simply spray it into one nostril while the person lies on their back. For the injection, follow the instructions provided, making sure to inject it into a muscle, under the skin, or directly into a vein if you’re trained to do so.
Side Effects of Narcan
While Narcan is generally safe, it can cause side effects, especially in people who are physically dependent on opioids. Common side effects include:
-
Withdrawal Symptoms: Narcan can rapidly push opioids out of the body, causing withdrawal symptoms like nausea, vomiting, sweating, shaking, and a fast heartbeat. These symptoms can be uncomfortable and, in some cases, severe.
-
Injection Site Reactions: If you administer Narcan as an injection, you might notice redness, swelling, or pain at the injection site. These reactions usually resolve on their own and are common with injectable medications.
-
Heart and Blood Pressure Changes: Narcan can cause temporary changes in heart rate or blood pressure. These changes are typically short-lived but should be monitored, especially by healthcare professionals in a medical setting.
-
Breathing Problems: In rare cases, Narcan can cause breathing issues, particularly if given to someone who does not have opioids in their system.
Serious Side Effects of Narcan
In rare instances, Narcan can cause serious side effects, especially in people with underlying health conditions or when given in repeated doses. Serious side effects might include:
-
Severe Withdrawal Symptoms: For individuals who are physically dependent on opioids, the sudden withdrawal caused by Narcan can be intense, leading to severe discomfort and distress.
-
Heart Complications: Narcan can occasionally cause irregular heartbeats or, in very rare cases, more severe heart problems. It’s important to be aware of this, particularly in individuals with existing heart conditions.
-
Severe Allergic Reactions: Although extremely rare, some people might experience severe allergic reactions to Narcan, including difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, and hives. Immediate medical attention is necessary if these symptoms occur.
Understanding the Effects of Narcan
When someone receives Narcan, they often wake up feeling disoriented and uncomfortable. They might experience nausea, headaches, or body aches. The effects of Narcan are typically short-lived, but they can be intense, especially for those who were unconscious during an overdose. Understanding the effects of Narcan can help you prepare for the possible reactions after its administration.
How Long Does Narcan Affect You?
The effects of Narcan usually last between 30 to 90 minutes. During this time, it counteracts the effects of opioids, helping to restore normal breathing and consciousness. However, because opioids can stay in the body longer than Narcan, the individual may need additional doses or further medical attention once the effects of Narcan wear off.
What Happens if You Take Narcan Without Needing It?
If you administer Narcan to someone who isn’t experiencing an opioid overdose, it generally won’t cause any serious harm. The person might feel some discomfort, but Narcan is designed to work specifically on opioid receptors, so without opioids present, it has little to no effect. This makes Narcan safe to use even if you’re not certain whether someone is overdosing.
Can You Abuse Narcan?
No, Narcan cannot be abused. It does not produce any euphoric effects or a "high," so there is no incentive for misuse. Narcan’s primary function is to reverse the life-threatening effects of opioids, and it doesn’t alter consciousness in a way that would make it attractive for abuse.
Drug Interactions and Considerations
Narcan is a safe and effective medication, but it’s important to be aware of potential drug interactions. If the person receiving Narcan has been using other substances, particularly those that affect the central nervous system, the response to Narcan might be different. Healthcare professionals should consider all potential interactions when treating someone for an overdose.
Does Narcan Work on Cocaine?
Narcan is specifically designed to reverse the effects of opioids and does not work on substances like cocaine or methamphetamines. If someone is overdosing on cocaine, Narcan will not be effective, and different medical interventions are needed. Understanding the difference between Narcan and other overdose treatments ensures the correct response in an emergency.
How Does Narcan Work Scientifically?
Narcan works by binding to the opioid receptors in the brain, blocking the effects of opioids and reversing the overdose. This scientific mechanism helps restore normal function in the central nervous system, which is crucial in emergencies. The rapid action of Narcan makes it an effective tool in saving lives during opioid overdoses.
Narcan’s Role in Addressing Opioid Use Disorder
Narcan plays a crucial role in addressing opioid use disorder by providing an emergency solution to overdosing on opioids. However, it’s also important to understand that Narcan is not a cure for opioid use disorder. It is a temporary measure to prevent death or serious harm during an overdose. Long-term treatment for opioid use disorder involves a combination of medication, therapy, and support.
Conclusion
Narcan is a critical tool in the fight against opioid overdoses. Understanding how it works, its potential side effects, and what to expect after administration is essential for anyone who might need to use it. Whether you’re a healthcare provider, first responder, or concerned individual, knowing how to properly use Narcan can save lives. Always seek medical advice and training to ensure you are prepared to use Narcan safely and effectively.


